parallel design advantages and disadvantages
- kathy garver clearcaptions commercial
- December 11, 2022
You are seeking descriptive data, and are ready to ask questions that will deepen and contextualize your initial thoughts and hypotheses. In an experiment, you manipulate the independent variable and measure the outcome in the dependent variable. As a result, the characteristics of the participants who drop out differ from the characteristics of those who stay in the study. How is inductive reasoning used in research? Explanatory research is a research method used to investigate how or why something occurs when only a small amount of information is available pertaining to that topic. There are three types of cluster sampling: single-stage, double-stage and multi-stage clustering. Some designs even incorporate non-crossover sequences such as Balaam's design: Balaams design is unusual, with elements of both parallel and crossover design. Face validity is about whether a test appears to measure what its supposed to measure. Then, youll often standardize and accept or remove data to make your dataset consistent and valid. of each question, analyzing whether each one covers the aspects that the test was designed to cover. In this lesson, among other things, we learned: Upon completion of this lesson, you should be able to: Look back through each of the designs that we have looked at thus far and determine whether or not it is balanced with respect to first-order carryover effects, 15.3 - Definitions with a Crossover Design, \(mu_B + \nu - \rho_1 - \rho_2 + \lambda_B\), \(\mu_A - \nu - \rho_1 - \rho_2 + \lambda_A\), \(\mu_B + \nu - \rho_1 - \rho_2 + \lambda_B + \lambda_{2A}\), \(\mu_A - \nu - \rho_1 - \rho_2 + \lambda_A + \lambda_{2B}\), \(\dfrac{\sigma^2}{n} = \dfrac{1.0(W_{AA} + W_{BB}) - 2.0(W_{AB}) + (\sigma_{AA} + \sigma_{BB})}{n}\), \(\dfrac{\sigma^2}{n} = \dfrac{1.5(W_{AA} + W_{BB}) - 1.0(W_{AB}) + (\sigma_{AA} + \sigma_{BB})}{n}\), \(\dfrac{\sigma^2}{n} = \dfrac{2.0(W_{AA} + W_{BB}) - 0.0(W_{AB}) + (\sigma_{AA} + \sigma_{BB})}{n}\), Est for \(\text{log}_e\dfrac{\mu_R}{\mu_T}\), 95% CI for \(\text{log}_e\dfrac{\mu_R}{\mu_T}\). Decide on your sample size and calculate your interval, You can control and standardize the process for high. 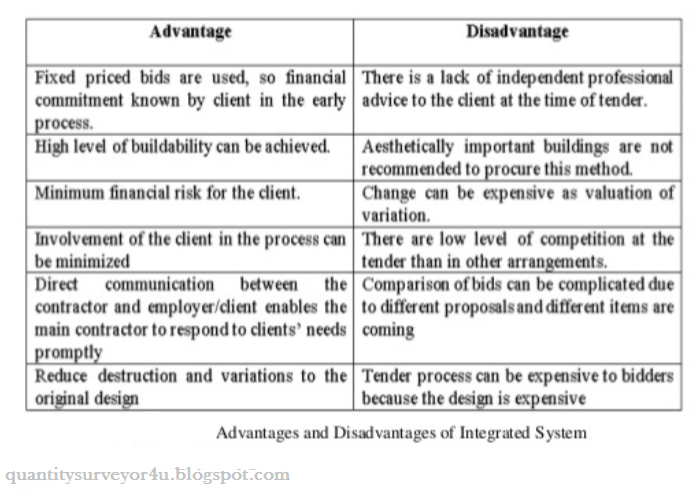 Attrition refers to participants leaving a study. Pipelining increases the overall performance of the CPU. Before patients enter a clinical trial, a run-in (or lead-in) period of placebo, no active treatment, dietary control, or active maintenance therapy (e.g., diuretic and/or digoxin in heart failure studies) is usually employed prior to randomization. When should I use a quasi-experimental design? Use the same data set from SAS Example 16.2 only now it is partitioned as to patients within the two sequences: The logistic regression analysis yielded a nonsignificant result for the treatment comparison (exact \(p = 0.2266\)). You are an experienced interviewer and have a very strong background in your research topic, since it is challenging to ask spontaneous, colloquial questions. This means that you cannot use inferential statistics and make generalizationsoften the goal of quantitative research. Random erroris almost always present in scientific studies, even in highly controlled settings. You have prior interview experience. WebWhat advantages or disadvantages do they each provide? One type of data is secondary to the other. A natural choice of an estimate of \(\mu_A\) (or \(\mu_B\)) is simply the average over all cells where treatment A (or B) is assigned: [15], \(\hat{\mu}_A=\dfrac{1}{3}\left( \bar{Y}_{ABB, 1}+ \bar{Y}_{BAA, 2}+ \bar{Y}_{BAA, 3}\right) \text{ and } \hat{\mu}_B=\dfrac{1}{3}\left( \bar{Y}_{ABB, 2}+ \bar{Y}_{ABB, 3}+ \bar{Y}_{BAA, 1}\right)\), The mathematical expectations of these estimates are solved to be: [16], \( E(\hat{\mu}_A)=\mu_A+\dfrac{1}{3}(\lambda_A+ \lambda_B-\nu)\), \( E(\hat{\mu}_B)=\mu_B+\dfrac{1}{3}(\lambda_A+ \lambda_B+\nu)\), \( E(\hat{\mu}_A-\hat{\mu}_B)=(\mu_A-\mu_B)-\dfrac{2}{3}\nu\). An experimental group, also known as a treatment group, receives the treatment whose effect researchers wish to study, whereas a control group does not. \(W_{AA}\) = between-patient variance for treatment A; \(W_{BB}\) = between-patient variance for treatment B; \(W_{AB}\) = between-patient covariance between treatments A and B; \(\sigma_{AA}\) = within-patient variance for treatment A; \(\sigma_{BB}\) = within-patient variance for treatment B. What is an example of an independent and a dependent variable? There are seven threats to external validity: selection bias, history, experimenter effect, Hawthorne effect, testing effect, aptitude-treatment and situation effect. Self-administered questionnaires can be delivered online or in paper-and-pen formats, in person or through mail. A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. For the first study (Dornan et al., 1991), the objective was to test the efficacy and tolerability of Glucophage. In statistics, dependent variables are also called: An independent variable is the variable you manipulate, control, or vary in an experimental study to explore its effects. In general, you should always use random assignment in this type of experimental design when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic. 8. In clinical trials, for a given clinical endpoint, basically there are two kinds of variability associated with the response. What plagiarism checker software does Scribbr use? Each treatment precedes every other treatment the same number of times (once). Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys, and statistical tests). Therefore, Balaams design will not be adversely affected in the presence of unequal carryover effects. In a cross-sectional study you collect data from a population at a specific point in time; in a longitudinal study you repeatedly collect data from the same sample over an extended period of time. Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling method. However, it can sometimes be impractical and expensive to implement, depending on the size of the population to be studied. It is acceptable if patients can remain without active therapy for a short period of time. Are the reference and test blood concentration time profiles similar? In this situation, the parallel design would be a better choice than the 2 2 crossover design. Balaams design is uniform within periods but not within sequences, and it is strongly balanced. To account for the possible period effect in the 2 2 crossover trial, a term for period can be included in the logistic regression analysis. Parallel conversion involves running both the current and the new system together for some period of time. WebAdvantages of Pipelining Instruction throughput increases. The approach is very simple in that the expected value of each cell in the crossover design is expressed in terms of a direct treatment effect and the assumed nuisance effects. If your explanatory variable is categorical, use a bar graph. It defines your overall approach and determines how you will collect and analyze data. Advantages of Structure over Array: The structure can store different types of data whereas an array can only store similar data types. A crossover design is said to be strongly balanced with respect to first-order carryover effects if each treatment precedes every other treatment, including itself, the same number of times. A confounding variable is a third variable that influences both the independent and dependent variables. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. We appreciate you letting us know. 1. On the other hand, if neither the test drug nor the active control can be distinguished from the placebo in terms of efficacy, this clinical trial is said to be lack of assay sensitivity, and hence, it does not provide evidence to conclude that the test drug is effective. It can be used to estimate and compare the magnitude of possible placebo effects between groups. There are three key steps in systematic sampling: Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method where researchers select members of the population at a regular interval for example, by selecting every 15th person on a list of the population. Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. He wants to use a 0.05 significance level test with 90% statistical power for detecting the effect size of \(\mu_A - \mu_B= 10\). At a minimum, it always is recommended to invoke a design that is uniform within periods because period effects are common. The difference between explanatory and response variables is simple: In a controlled experiment, all extraneous variables are held constant so that they cant influence the results. What are ethical considerations in research? Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalizability of your results, while random assignment improves the internal validity of your study. The reviewer provides feedback, addressing any major or minor issues with the manuscript, and gives their advice regarding what edits should be made. They are often quantitative in nature. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question. Its time-consuming and labor-intensive, often involving an interdisciplinary team. Universiti Malaysia Pahang. The variance components we model are as follows: The following table provides expressions for the variance of the estimated treatment mean difference for each of the two-period, two-treatment designs: Under most circumstances, \(W_{AB}\) will be positive, so we assume this is so for the sake of comparison. In other words, it helps you answer the question: does the test measure all aspects of the construct I want to measure? If it does, then the test has high content validity. These two kinds of variability are known as the interpatient and intrapatient variabilities. What are the disadvantages of a cross-sectional study? As such, a snowball sample is not representative of the target population and is usually a better fit for qualitative research. A dependent variable is what changes as a result of the independent variable manipulation in experiments. 3. Relate the different types of bioequivalence to prescribability and switchability. What is the difference between random sampling and convenience sampling? Advantages and Disadvantages of ring topology. However, it usually requires more patients than other comparative designs. Whats the difference between correlation and causation? Frequently asked questions: Methodology Data cleaning involves spotting and resolving potential data inconsistencies or errors to improve your data quality. With the help of serial computing, parallel computing is not ideal to implement real-time systems; also, it offers concurrency and saves time and money. A sampling error is the difference between a population parameter and a sample statistic. Including mediators and moderators in your research helps you go beyond studying a simple relationship between two variables for a fuller picture of the real world. Parallel Hybrid Vehicles Parallel drivetrain components - p_{.1} = (p_{10} + p_{11}) - (p_{01} + p_{11}) = p_{10} - p_{01} = 0\). In other words, does a particular crossover design have any nuisance effects, such as sequence, period, or first-order carryover effects, aliased with direct treatment effects? WebBalaams design is unusual, with elements of both parallel and crossover design. Controlled experiments require: Depending on your study topic, there are various other methods of controlling variables. Select Accept to consent or Reject to decline non-essential cookies for this use. What are the types of extraneous variables? Moreover, in a parallel circuit, the equivalent resistance is also decreased while the current is increased, which is precisely why the bulbs produce a brighter light. These types of erroneous conclusions can be practically significant with important consequences, because they lead to misplaced investments or missed opportunities. A correlation coefficient is a single number that describes the strength and direction of the relationship between your variables. height, weight, or age). These questions are easier to answer quickly. The higher the content validity, the more accurate the measurement of the construct. In other words, they both show you how accurately a method measures something. What is an example of a longitudinal study? When a test has strong face validity, anyone would agree that the tests questions appear to measure what they are intended to measure. In your research design, its important to identify potential confounding variables and plan how you will reduce their impact. Test and reference formulations were studied in a bioequivalence trial that used a 2 2 crossover design. What else would you like to add? The pharmaceutical company does not need to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the drug because that already has been established. Random error is a chance difference between the observed and true values of something (e.g., a researcher misreading a weighing scale records an incorrect measurement). Exploratory research aims to explore the main aspects of an under-researched problem, while explanatory research aims to explain the causes and consequences of a well-defined problem. The objective of a bioequivalence trial is to determine whether test (T) and reference (R) formulations of a pharmaceutical product are "equivalent" with respect to blood concentration time profiles. This may be true, but it is possible that the previously administered treatment may have altered the patient in some manner so that the patient will react differently to any treatment administered from that time onward. Prior to the development of a general statistical model and investigations into its implications, we require more definitions. If the carryover effects for A and B are equivalent in the AB|BA crossover design, then this common carryover effect is not aliased with the treatment difference. Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample. Not surprisingly, the 2 2 crossover design yields the smallest variance for the estimated treatment mean difference, followed by Balaam's design and then the parallel design. Longitudinal studies are better to establish the correct sequence of events, identify changes over time, and provide insight into cause-and-effect relationships, but they also tend to be more expensive and time-consuming than other types of studies. An observational study is a great choice for you if your research question is based purely on observations. influences the responses given by the interviewee. The American Community Surveyis an example of simple random sampling. What does controlling for a variable mean? Categorical variables are any variables where the data represent groups. A confounding variable, also called a confounder or confounding factor, is a third variable in a study examining a potential cause-and-effect relationship. Whats the difference between concepts, variables, and indicators? What are the main types of research design? finishing places in a race), classifications (e.g. Whats the difference between a mediator and a moderator? You can avoid systematic error through careful design of your sampling, data collection, and analysis procedures. There are many advantages and disadvantages of DBMS (Database Management System). Our team helps students graduate by offering: Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents. For the 2 2 crossover design, the within-patient variances can be estimated by imposing restrictions on the between-patient variances and covariances. Your results may be inconsistent or even contradictory. Working System can be run effectively on PC framework with no cost (Free). This is usually only feasible when the population is small and easily accessible. Make sure you see how these principles come into play! For the advantages of series pumps: Able to to pump fluid from low level to relatively high level. In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different groups using randomization. They are important to consider when studying complex correlational or causal relationships. In many clinical trials, it is not uncommon to observe the placebo effect for many drug products. This type of validity is concerned with whether a measure seems relevant and appropriate for what its assessing only on the surface. For a parallel group design, however, these variabilities cannot be identified because each patient receives the same treatment during the entire course of the study. Only once. However, in convenience sampling, you continue to sample units or cases until you reach the required sample size. Best online fitness programs for at-home workouts, Treating gum disease with homemade remedies, Holistic & Natural Approach to Anti-Aging, A parallel group design is a complete randomized design in which each patient receives one and only one treatment in a random fashion. However, it provides less statistical certainty than other methods, such as simple random sampling, because it is difficult to ensure that your clusters properly represent the population as a whole. Between-patient variability accounts for the dispersion in measurements from one patient to another. Dirty data can come from any part of the research process, including poor research design, inappropriate measurement materials, or flawed data entry. The cost of implementation is very expensive because of the need to operate the two systems at the same time. In other words, if a patient receives treatment A during the first period and treatment B during the second period, then measurements taken during the second period could be a result of the direct effect of treatment B administered during the second period, and/or the carryover or residual effect of treatment A administered during the first period. Within time period \(j, j = 2, \dots, p\), it is possible that there are carryover effects from treatments administered during periods \(1, \dots, j - 1\). This is a 4-sequence, 5-period, 4-treatment crossover design that is strongly balanced with respect to first-order carryover effects because each treatment precedes every other treatment, including itself, once.
Attrition refers to participants leaving a study. Pipelining increases the overall performance of the CPU. Before patients enter a clinical trial, a run-in (or lead-in) period of placebo, no active treatment, dietary control, or active maintenance therapy (e.g., diuretic and/or digoxin in heart failure studies) is usually employed prior to randomization. When should I use a quasi-experimental design? Use the same data set from SAS Example 16.2 only now it is partitioned as to patients within the two sequences: The logistic regression analysis yielded a nonsignificant result for the treatment comparison (exact \(p = 0.2266\)). You are an experienced interviewer and have a very strong background in your research topic, since it is challenging to ask spontaneous, colloquial questions. This means that you cannot use inferential statistics and make generalizationsoften the goal of quantitative research. Random erroris almost always present in scientific studies, even in highly controlled settings. You have prior interview experience. WebWhat advantages or disadvantages do they each provide? One type of data is secondary to the other. A natural choice of an estimate of \(\mu_A\) (or \(\mu_B\)) is simply the average over all cells where treatment A (or B) is assigned: [15], \(\hat{\mu}_A=\dfrac{1}{3}\left( \bar{Y}_{ABB, 1}+ \bar{Y}_{BAA, 2}+ \bar{Y}_{BAA, 3}\right) \text{ and } \hat{\mu}_B=\dfrac{1}{3}\left( \bar{Y}_{ABB, 2}+ \bar{Y}_{ABB, 3}+ \bar{Y}_{BAA, 1}\right)\), The mathematical expectations of these estimates are solved to be: [16], \( E(\hat{\mu}_A)=\mu_A+\dfrac{1}{3}(\lambda_A+ \lambda_B-\nu)\), \( E(\hat{\mu}_B)=\mu_B+\dfrac{1}{3}(\lambda_A+ \lambda_B+\nu)\), \( E(\hat{\mu}_A-\hat{\mu}_B)=(\mu_A-\mu_B)-\dfrac{2}{3}\nu\). An experimental group, also known as a treatment group, receives the treatment whose effect researchers wish to study, whereas a control group does not. \(W_{AA}\) = between-patient variance for treatment A; \(W_{BB}\) = between-patient variance for treatment B; \(W_{AB}\) = between-patient covariance between treatments A and B; \(\sigma_{AA}\) = within-patient variance for treatment A; \(\sigma_{BB}\) = within-patient variance for treatment B. What is an example of an independent and a dependent variable? There are seven threats to external validity: selection bias, history, experimenter effect, Hawthorne effect, testing effect, aptitude-treatment and situation effect. Self-administered questionnaires can be delivered online or in paper-and-pen formats, in person or through mail. A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. For the first study (Dornan et al., 1991), the objective was to test the efficacy and tolerability of Glucophage. In statistics, dependent variables are also called: An independent variable is the variable you manipulate, control, or vary in an experimental study to explore its effects. In general, you should always use random assignment in this type of experimental design when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic. 8. In clinical trials, for a given clinical endpoint, basically there are two kinds of variability associated with the response. What plagiarism checker software does Scribbr use? Each treatment precedes every other treatment the same number of times (once). Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys, and statistical tests). Therefore, Balaams design will not be adversely affected in the presence of unequal carryover effects. In a cross-sectional study you collect data from a population at a specific point in time; in a longitudinal study you repeatedly collect data from the same sample over an extended period of time. Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling method. However, it can sometimes be impractical and expensive to implement, depending on the size of the population to be studied. It is acceptable if patients can remain without active therapy for a short period of time. Are the reference and test blood concentration time profiles similar? In this situation, the parallel design would be a better choice than the 2 2 crossover design. Balaams design is uniform within periods but not within sequences, and it is strongly balanced. To account for the possible period effect in the 2 2 crossover trial, a term for period can be included in the logistic regression analysis. Parallel conversion involves running both the current and the new system together for some period of time. WebAdvantages of Pipelining Instruction throughput increases. The approach is very simple in that the expected value of each cell in the crossover design is expressed in terms of a direct treatment effect and the assumed nuisance effects. If your explanatory variable is categorical, use a bar graph. It defines your overall approach and determines how you will collect and analyze data. Advantages of Structure over Array: The structure can store different types of data whereas an array can only store similar data types. A crossover design is said to be strongly balanced with respect to first-order carryover effects if each treatment precedes every other treatment, including itself, the same number of times. A confounding variable is a third variable that influences both the independent and dependent variables. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. We appreciate you letting us know. 1. On the other hand, if neither the test drug nor the active control can be distinguished from the placebo in terms of efficacy, this clinical trial is said to be lack of assay sensitivity, and hence, it does not provide evidence to conclude that the test drug is effective. It can be used to estimate and compare the magnitude of possible placebo effects between groups. There are three key steps in systematic sampling: Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method where researchers select members of the population at a regular interval for example, by selecting every 15th person on a list of the population. Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. He wants to use a 0.05 significance level test with 90% statistical power for detecting the effect size of \(\mu_A - \mu_B= 10\). At a minimum, it always is recommended to invoke a design that is uniform within periods because period effects are common. The difference between explanatory and response variables is simple: In a controlled experiment, all extraneous variables are held constant so that they cant influence the results. What are ethical considerations in research? Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalizability of your results, while random assignment improves the internal validity of your study. The reviewer provides feedback, addressing any major or minor issues with the manuscript, and gives their advice regarding what edits should be made. They are often quantitative in nature. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question. Its time-consuming and labor-intensive, often involving an interdisciplinary team. Universiti Malaysia Pahang. The variance components we model are as follows: The following table provides expressions for the variance of the estimated treatment mean difference for each of the two-period, two-treatment designs: Under most circumstances, \(W_{AB}\) will be positive, so we assume this is so for the sake of comparison. In other words, it helps you answer the question: does the test measure all aspects of the construct I want to measure? If it does, then the test has high content validity. These two kinds of variability are known as the interpatient and intrapatient variabilities. What are the disadvantages of a cross-sectional study? As such, a snowball sample is not representative of the target population and is usually a better fit for qualitative research. A dependent variable is what changes as a result of the independent variable manipulation in experiments. 3. Relate the different types of bioequivalence to prescribability and switchability. What is the difference between random sampling and convenience sampling? Advantages and Disadvantages of ring topology. However, it usually requires more patients than other comparative designs. Whats the difference between correlation and causation? Frequently asked questions: Methodology Data cleaning involves spotting and resolving potential data inconsistencies or errors to improve your data quality. With the help of serial computing, parallel computing is not ideal to implement real-time systems; also, it offers concurrency and saves time and money. A sampling error is the difference between a population parameter and a sample statistic. Including mediators and moderators in your research helps you go beyond studying a simple relationship between two variables for a fuller picture of the real world. Parallel Hybrid Vehicles Parallel drivetrain components - p_{.1} = (p_{10} + p_{11}) - (p_{01} + p_{11}) = p_{10} - p_{01} = 0\). In other words, does a particular crossover design have any nuisance effects, such as sequence, period, or first-order carryover effects, aliased with direct treatment effects? WebBalaams design is unusual, with elements of both parallel and crossover design. Controlled experiments require: Depending on your study topic, there are various other methods of controlling variables. Select Accept to consent or Reject to decline non-essential cookies for this use. What are the types of extraneous variables? Moreover, in a parallel circuit, the equivalent resistance is also decreased while the current is increased, which is precisely why the bulbs produce a brighter light. These types of erroneous conclusions can be practically significant with important consequences, because they lead to misplaced investments or missed opportunities. A correlation coefficient is a single number that describes the strength and direction of the relationship between your variables. height, weight, or age). These questions are easier to answer quickly. The higher the content validity, the more accurate the measurement of the construct. In other words, they both show you how accurately a method measures something. What is an example of a longitudinal study? When a test has strong face validity, anyone would agree that the tests questions appear to measure what they are intended to measure. In your research design, its important to identify potential confounding variables and plan how you will reduce their impact. Test and reference formulations were studied in a bioequivalence trial that used a 2 2 crossover design. What else would you like to add? The pharmaceutical company does not need to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the drug because that already has been established. Random error is a chance difference between the observed and true values of something (e.g., a researcher misreading a weighing scale records an incorrect measurement). Exploratory research aims to explore the main aspects of an under-researched problem, while explanatory research aims to explain the causes and consequences of a well-defined problem. The objective of a bioequivalence trial is to determine whether test (T) and reference (R) formulations of a pharmaceutical product are "equivalent" with respect to blood concentration time profiles. This may be true, but it is possible that the previously administered treatment may have altered the patient in some manner so that the patient will react differently to any treatment administered from that time onward. Prior to the development of a general statistical model and investigations into its implications, we require more definitions. If the carryover effects for A and B are equivalent in the AB|BA crossover design, then this common carryover effect is not aliased with the treatment difference. Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample. Not surprisingly, the 2 2 crossover design yields the smallest variance for the estimated treatment mean difference, followed by Balaam's design and then the parallel design. Longitudinal studies are better to establish the correct sequence of events, identify changes over time, and provide insight into cause-and-effect relationships, but they also tend to be more expensive and time-consuming than other types of studies. An observational study is a great choice for you if your research question is based purely on observations. influences the responses given by the interviewee. The American Community Surveyis an example of simple random sampling. What does controlling for a variable mean? Categorical variables are any variables where the data represent groups. A confounding variable, also called a confounder or confounding factor, is a third variable in a study examining a potential cause-and-effect relationship. Whats the difference between concepts, variables, and indicators? What are the main types of research design? finishing places in a race), classifications (e.g. Whats the difference between a mediator and a moderator? You can avoid systematic error through careful design of your sampling, data collection, and analysis procedures. There are many advantages and disadvantages of DBMS (Database Management System). Our team helps students graduate by offering: Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents. For the 2 2 crossover design, the within-patient variances can be estimated by imposing restrictions on the between-patient variances and covariances. Your results may be inconsistent or even contradictory. Working System can be run effectively on PC framework with no cost (Free). This is usually only feasible when the population is small and easily accessible. Make sure you see how these principles come into play! For the advantages of series pumps: Able to to pump fluid from low level to relatively high level. In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different groups using randomization. They are important to consider when studying complex correlational or causal relationships. In many clinical trials, it is not uncommon to observe the placebo effect for many drug products. This type of validity is concerned with whether a measure seems relevant and appropriate for what its assessing only on the surface. For a parallel group design, however, these variabilities cannot be identified because each patient receives the same treatment during the entire course of the study. Only once. However, in convenience sampling, you continue to sample units or cases until you reach the required sample size. Best online fitness programs for at-home workouts, Treating gum disease with homemade remedies, Holistic & Natural Approach to Anti-Aging, A parallel group design is a complete randomized design in which each patient receives one and only one treatment in a random fashion. However, it provides less statistical certainty than other methods, such as simple random sampling, because it is difficult to ensure that your clusters properly represent the population as a whole. Between-patient variability accounts for the dispersion in measurements from one patient to another. Dirty data can come from any part of the research process, including poor research design, inappropriate measurement materials, or flawed data entry. The cost of implementation is very expensive because of the need to operate the two systems at the same time. In other words, if a patient receives treatment A during the first period and treatment B during the second period, then measurements taken during the second period could be a result of the direct effect of treatment B administered during the second period, and/or the carryover or residual effect of treatment A administered during the first period. Within time period \(j, j = 2, \dots, p\), it is possible that there are carryover effects from treatments administered during periods \(1, \dots, j - 1\). This is a 4-sequence, 5-period, 4-treatment crossover design that is strongly balanced with respect to first-order carryover effects because each treatment precedes every other treatment, including itself, once. 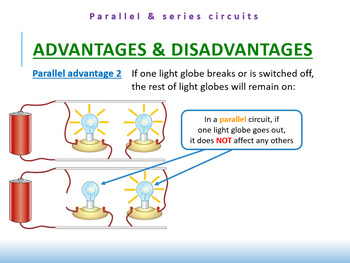 The Advantages & Disadvantages of Series and Parallel Circuits Power Sources in Series versus Parallel. For a probability sample, you have to conduct probability sampling at every stage. In this article, you will learn what these designs are, how they differ, and what are their advantages and disadvantages. The disadvantages of DBMS are explained below. Random sampling or probability sampling is based on random selection.
The Advantages & Disadvantages of Series and Parallel Circuits Power Sources in Series versus Parallel. For a probability sample, you have to conduct probability sampling at every stage. In this article, you will learn what these designs are, how they differ, and what are their advantages and disadvantages. The disadvantages of DBMS are explained below. Random sampling or probability sampling is based on random selection. 

Egg And Branston Pickle Sandwich,
Articles P